Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Transforming the Digital Future
Wed Nov 01 2025

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are no longer futuristic concepts confined to research labs or science fiction. They have become foundational technologies powering modern digital transformation across industries. From personalized recommendations on streaming platforms to fraud detection in banking and autonomous vehicles on the road, AI and ML are reshaping how businesses operate and how people interact with technology.
This article explores what AI and ML are, how they work, their real-world applications, challenges, and what the future holds.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence refers to the broader concept of machines being able to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, problem-solving, understanding language, recognizing patterns, and making decisions.
AI systems can be broadly classified into three categories:
1. Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI is designed to perform a specific task extremely well. Examples include:
- Voice assistants like Siri or Alexa
- Recommendation engines on e-commerce platforms
- Spam filters in email systems
Almost all AI systems in use today fall under this category.
2. General AI (Strong AI)
General AI refers to systems that can understand, learn, and apply intelligence across a wide range of tasks at a human level. This form of AI does not yet exist and remains a long-term research goal.
3. Super AI
Super AI would surpass human intelligence in every aspect, including creativity and emotional intelligence. This concept remains theoretical and raises important ethical and philosophical questions.
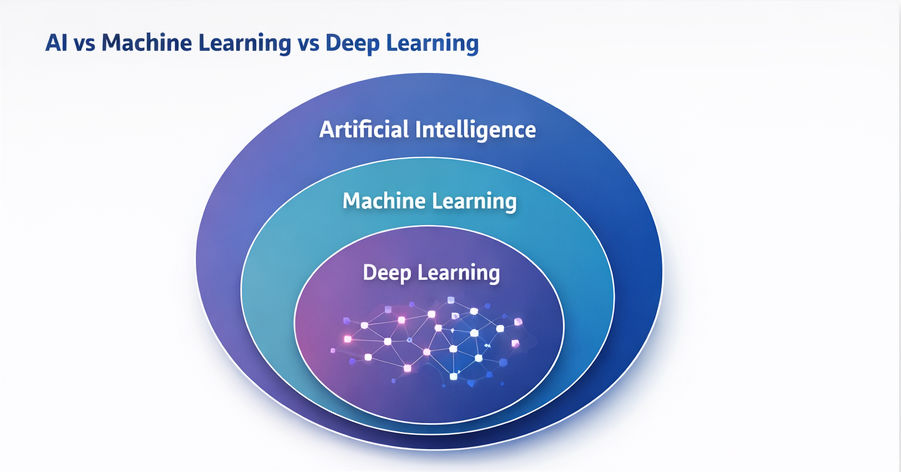
What Is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on enabling machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of following rigid rules, ML models identify patterns in data and improve their performance over time.
At its core, ML relies on:
- Data
- Algorithms
- Computational power
The more high-quality data a system has, the better it can learn and make accurate predictions.
Types of Machine Learning
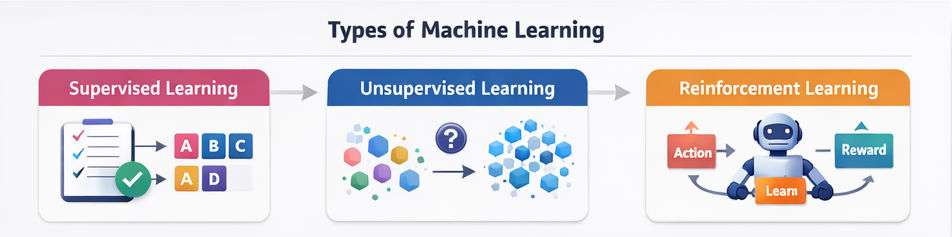
1. Supervised Learning
In supervised learning, models are trained using labeled data. Each input comes with a corresponding correct output.
Common use cases include:
- Email spam detection
- Image classification
- Price prediction
Popular algorithms:
- Linear Regression
- Logistic Regression
- Decision Trees
- Support Vector Machines
- Neural Networks
2. Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data. The model discovers hidden patterns or structures on its own.
Use cases include:
- Customer segmentation
- Anomaly detection
- Market basket analysis
Common algorithms:
- K-Means Clustering
- Hierarchical Clustering
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Semi-Supervised Learning
This approach combines a small amount of labeled data with a large amount of unlabeled data. It is useful when labeling data is expensive or time-consuming.
4. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning involves an agent that learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties based on its actions.
Applications include:
- Game playing (e.g., AlphaGo)
- Robotics
- Autonomous vehicles
- Dynamic pricing systems
Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Deep Learning is a specialized branch of ML that uses artificial neural networks inspired by the human brain. These networks consist of multiple layers (hence “deep”) that progressively extract higher-level features from data.
Key deep learning architectures include:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image and video processing
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for sequential data
- Transformers for natural language processing and generative AI
Deep learning has driven major breakthroughs in speech recognition, image generation, language translation, and large language models.
Real-World Applications of AI and ML
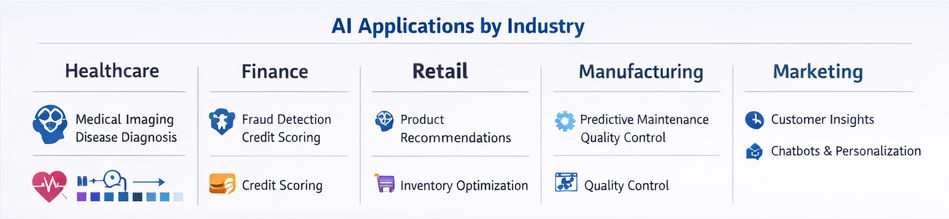
Healthcare
- Disease prediction and diagnosis
- Medical image analysis
- Drug discovery
- Personalized treatment plans
Finance
- Fraud detection
- Credit scoring
- Algorithmic trading
- Risk assessment
Retail and E-commerce
- Product recommendations
- Demand forecasting
- Inventory optimization
- Dynamic pricing
Manufacturing
- Predictive maintenance
- Quality inspection using computer vision
- Supply chain optimization
Marketing and Customer Experience
- Customer behavior analysis
- Chatbots and virtual assistants
- Sentiment analysis
- Personalized campaigns
Transportation
- Autonomous vehicles
- Route optimization
- Traffic prediction
Benefits of AI and ML
- Automation of repetitive tasks
- Improved decision-making through data insights
- Scalability and efficiency
- Personalized user experiences
- Cost reduction and productivity gains
Organizations that successfully adopt AI gain a strong competitive advantage by responding faster to market changes and customer needs.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, AI and ML face several challenges:
Data Quality and Bias
Models are only as good as the data they are trained on. Biased or incomplete data can lead to unfair or inaccurate outcomes.
Explainability
Many advanced models, especially deep learning systems, function as “black boxes,” making it difficult to explain how decisions are made.
Security and Privacy
AI systems often rely on sensitive data, raising concerns about data privacy, misuse, and compliance with regulations.
High Implementation Costs
Developing and maintaining AI systems requires skilled talent, infrastructure, and continuous monitoring.
Ethical Concerns
Issues such as job displacement, surveillance, and misuse of AI technologies must be addressed responsibly.
The Future of AI and ML
The future of AI and ML is both exciting and transformative. Key trends include:
- Generative AI producing text, images, code, and video
- AI copilots assisting developers, designers, and business users
- Edge AI enabling real-time intelligence on devices
- Responsible AI focusing on transparency, fairness, and governance
- AI democratization through low-code and no-code platforms
As AI becomes more embedded in everyday systems, collaboration between humans and intelligent machines will define the next era of innovation.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are reshaping industries, redefining business models, and transforming how we interact with technology. While challenges remain, the potential benefits far outweigh the risks when AI is developed and deployed responsibly.
Organizations that invest in AI today—by building data-driven cultures, upskilling talent, and focusing on ethical implementation—will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly intelligent digital world.
AI is not about replacing humans; it is about augmenting human capabilities and unlocking new possibilities for innovation and growth.
